

albedo - how much light a planet, satellite, or other nonluminous object reflects. Astronomers measure albedo from 0 to 1. A perfect reflector would have an albedo of 1.0; a black surface which absorbs all light would have an albedo of 0.0.
altitude - how high a point or celestial object is above or below the horizon. It ranges from 0 (on the horizon) to 90 (overhead). Negative values correspond to objects below the horizon.
aphelion - planets, comets, and asteroids travel around the Sun on paths called orbits. Although most people picture an orbit as a circle, in reality they are slightly stretched out into a figure called an ellipse. So, the object moves around the Sun at different distances, sometimes closer and sometimes farther away. Aphelion is the position of an object that orbits the Sun when it is farthest from the Sun.
apogee - The Moon travels around Earth on a path called an orbit. Although most people picture its orbit as a circle, in reality the Moon's path around our planet is slightly stretched out into a figure called an ellipse. So, it moves around Earth at different distances, sometimes closer and sometimes farther away. Apogee is the position of the Moon or any object (like an artificial satellite) that orbits Earth when it is furthest from Earth.
asteroid - also known as "minor planet"; one of millions of small bodies that orbit the Sun, which are not planets or comets. As of 2016, astronomers had archived the orbits of 709,706 asteroids, most of which lie in a region called the asteroid belt (see the next entry).
asteroid belt - an area between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where most of the asteroids are found.
astronomical unit - the average distance from Earth to the Sun. Astronomers have defined this distance as exactly 92,955,807.3 miles (149,597,870.7 kilometers).
astronomy - the study (both observational and theoretical) of the physical and chemical properties of celestial objects which inhabit the universe, or of the universe as a whole.
aurora - a glow in a planet's upper atmosphere caused by the interaction between the planet's magnetic field and charged particles from the Sun (the solar wind). We call it the aurora borealis when it appears in the Northern Hemisphere and the aurora australis when it appears in the Southern Hemisphere.
Baily's beads - tiny points of sunlight seen just before and just after the total phase of a solar eclipse. Gaps and irregularities in the Moon's surface cause this.
Cassini Division - a relatively empty area of Saturn's ring system, 2,600 miles (4,200 kilometers) wide, located between the A and B rings.
chromosphere - the region of the Sun's atmosphere between its photosphere and its corona.
comet - one of many relatively small solar system objects composed of frozen gases and dust that orbit the Sun.
constellation - one of the 88 imaginary figures made of stars that cover the sky. In 1928, a committee of astronomers formalized the constellation borders so there are no spaces between constellations, no overlaps, and no "shared" stars.
corona - the thin shell of illuminated gas that extends out some distance from the surface of the Sun.
craters - roughly circular depressions on the surface of many objects in the solar system; most craters were created when a meteorite hit. The rest were made by volcanoes or caused by surface collapse.
crescent - a phase of the Moon or other celestial body where the percent of visible surface illumination is more than 0 percent but less than 25 percent as seen from Earth.
 |
Members aboard Expedition 24 to the International Space Station |
day - one rotation (spin) of a planet on its axis.
diameter - the length from the surface of a celestial object, through its center, to the surface on the other side.
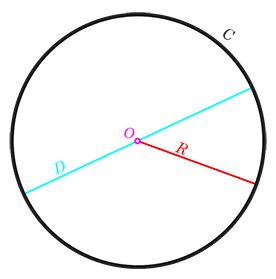 |
Measurements of a circle. The length of D is the diameter; |
diamond ring - the effect just before second contact or just after third contact of a total solar eclipse when a small portion of the Sun's surface plus the corona look like a ring with a brilliant diamond.
eclipse - when one celestial object's shadow falls on another object. The first object blocks out the Sun at the location where the shadow falls. The blocking of the Sun may be total or partial.
first contact - during a total solar eclipse, the moment that the Moon first touches the Sun. This marks the beginning of the eclipse.
First Quarter - the Moon's phase approximately a week after New Moon and a week before Full Moon, at which half of the side facing Earth is visible to us.
fourth contact - during a total solar eclipse, the moment the Moon breaks contact with the Sun; the end of the eclipse.
Full - a phase of the Moon when we see 100 percent of the side facing Earth.
gibbous - the Moon's phase when the percent we see is greater than 50 percent but less than 100 percent.
gravity - the attractive force of all bodies possessing mass.
Great Red Spot - an oval-shaped storm in Jupiter's atmosphere located 22 south of Jupiter's equator.
inner planets - planets closer to the Sun than the asteroid belt; Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
Last Quarter - the Moon's phase approximately a week after Full Moon and a week before New Moon when we see half of the side facing Earth.
lunar - of or pertaining to the Moon.
lunar eclipse - an eclipse that happens at Full Moon when the Moon passes either totally or partly through Earth's shadow.
meteor - a streak of light in the night sky caused by a tiny piece of rock or metal entering Earth's upper atmosphere and burning due to friction with the atmosphere; sometimes called a "shooting star" or "falling star."
meteor shower - what happens when Earth passes through a meteoroid stream; meteor showers happen every year on the same dates.
meteorite - any meteoroid which (after becoming a meteor) lands on the surface of the Earth.
meteoroid - small bodies made of rock, metal, or a combination of both which orbit the Sun; most are extremely small, with masses between one-thousandth and one-millionth of a gram.
moon - a naturally occurring, relatively large body that orbits a planet.
New - the Moon's phase when it lies between Earth and the Sun; during this phase, the Moon cannot be seen.
orbit - the path of a celestial object around another object.
outer planets - planets further from the Sun than the asteroid belt; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto.
penumbra - the less dark outer region of the Moon's shadow when it falls on Earth or Earth's shadow when it falls on the Sun.
penumbral eclipse - a lunar eclipse during which the Moon never enters the darker, inner part of the Earth's shadow, but remains in the outer, lighter penumbra.
perigee - the position of an object orbiting Earth when it is closest to Earth.
perihelion - the position of an object orbiting the Sun when it is closest to the Sun.
phase - the percent of the face of the Moon or other solar system object that we can see at any time in its orbit.
photosphere - the surface of the Sun and the part that gives off visible light.
planet - one of the eight main solar system objects that orbit the Sun and shine by reflected light.
prominence - a large-scale, gaseous formation above the surface of the Sun, usually over regions of solar activity such as sunspot groups.
rotation - the spinning motion of a planet or other celestial object around an axis.
satellite - a body that orbits a larger body.
solar - of or pertaining to the Sun.
solar eclipse - an eclipse at New Moon when the Moon covers the disk of the Sun, either totally or partially, for locations on Earth.
Sun - the star at the center of the solar system, around which Earth and the other planets orbit.
sunrise - the moment when the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon as a result of Earth's rotation.
sunset - the moment when the upper edge of the Sun disappears below the horizon as a result of Earth's rotation.
sunspot - a cool region on the Sun's surface caused by magnetic field variations.
terminator - the boundary between the sunlit and dark parts of the Moon. At the terminator, either sunrise or sunset is occurring.
terrestrial - of or pertaining to Earth.
third contact - during a total solar eclipse, the moment that the Moon last touches the Sun. This marks the end of the eclipse.
total eclipse - an eclipse of the Sun or Moon in which 1) the Sun is totally covered by the Moon; or 2) Earth's shadow totally covers the Moon.
umbra - the dark inner part of the shadow of Earth or the Moon.
waning - the time when the lit part of the Moon is getting smaller.
waxing - the time when the lit part of the Moon is growing larger.
year - the time it takes Earth or any planet to make one complete orbit around the Sun.